Understanding Search Engines and Their Operations
Search engines function as information systems that explore, comprehend, and structure online content to gives relevant results to users’ queries. For your content to appear in search engine results, it must be accessible to search engine crawlers, making it an integral part of SEO. The operations of search engines revolve around three primary functions:
1. Crawling: Search engines check the web for content, scrutinizing code and content for each URL they encounter.
2. Indexing: Content discovered during crawling is stored and arranged in an index, making it eligible for display in search results.
3. Ranking: Search engines prioritize and present the most relevant content to address users’ queries, ranking results based on relevance.
I’m Adeshola Adeshola, an SEO specialist and digital marketing consultant in London. If you prefer video content, here’s a tutorial from my YouTube channel on this topic.
Importance of Crawling and Indexing
For your content to be discoverable by users, ensuring its accessibility to crawlers and indexability is very important. Failure to do so renders it invisible to search engines. Crawling, the initial phase, involves search engine robots (crawlers or spiders) traversing the web to locate new and updated content, primarily through links. These robots navigate from one page to another, uncovering fresh content and incorporating it into their index, constituting a vast database of discovered URLs.
Search Engine Index and Ranking
A search engine index serves as an extensive repository housing all the content deemed suitable for presentation to users. During a search query, search engines search their index for highly relevant content and arrange it by relevance, a process known as ranking. The positioning of a website in search results directly correlates with the perceived relevance of its content to the query.
Optimizing for Crawl Budget and Steering Search Engine Activity
Crawl budget is the average number of URLs Googlebot crawls on a site before departure. Optimizing crawl budget ensures efficient utilization of Googlebot’s resources, preventing wasteful search of insignificant pages at the expense of crucial ones. This optimization holds particular significance for expansive websites harboring tens of thousands of URLs. Webmasters can influence search engine crawling through directives such as robots.txt files, delineating which sections of the site search engines should or shouldn’t crawl, alongside dictating crawling pace.
Common Issues Affecting Search Engine Visibility
1. New Websites Not Yet Indexed: Freshly launched websites might not have been explored by search engines due to limited external connections or submission.
– Fix: Speed up indexing by submitting the site to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools, or gain visibility through social media shares and links from trustworthy sites.
2. Lack of External Links: Websites without outside links may struggle to appear in search results.
– Fix: Get links from reputable sources by creating content, guest blogging, or building links.
3. Confusing Navigation: Complex website navigation makes it hard for search engines to find and index content.
– Fix: Simplify navigation and use tools like Google Search Console’s “Fetch as Google” to check crawlability.
4. Blocking Search Engine Access: Directives like robots.txt or meta robots tags can stop search engines from seeing certain pages, hindering indexing.
– Fix: Review directives to ensure important content isn’t blocked, using tools like Google Search Console’s “Robots.txt Tester” for confirmation.
5. Penalties for Unethical Practices: Websites penalized for actions like keyword stuffing or buying links may struggle to get indexed. – Fix: Clean up any spammy content or links, and ask for reconsideration from the search engine.
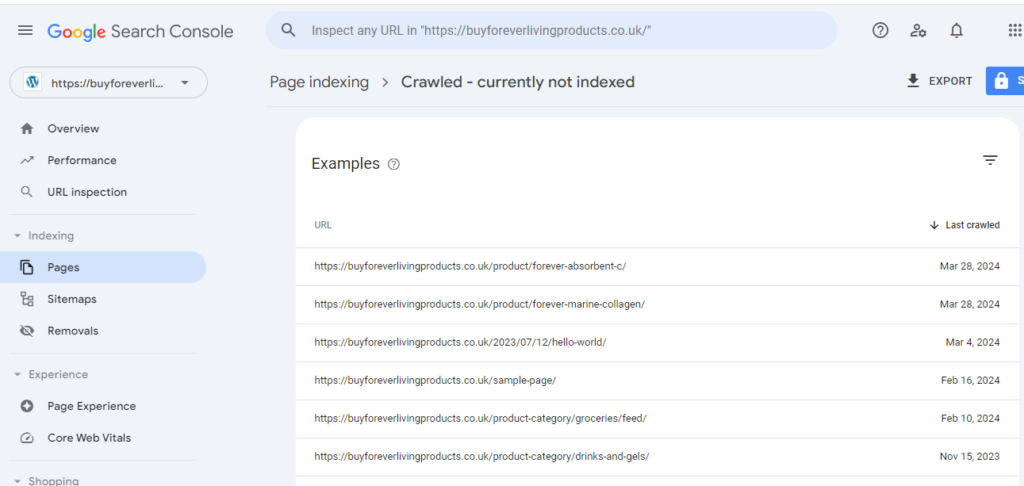
Strategies to Tackle These Challenges:
1. Use Google Search Console or Advanced Search Tricks: Use Google Search Console to find indexed pages and the “site:” search trick to spot unindexed content.
2. Guide Googlebot with Directives: Use optimization methods like managing crawl budget, internal linking, and clear navigation to influence Googlebot’s behavior.
3. Direct Googlebot with Robots.txt: Use robots.txt to steer search engine crawlers away from unwanted pages or areas.
4. Optimize Crawl Budget: Manage the website’s crawl budget to stop Googlebot from wasting resources on insignificant pages.
5. Clear Navigation for Search Engines: Help search engines navigate your site by providing clear and intuitive navigation structures with internal links.
Additional Optimization Recommendations:
1. Sitemap Usage: Implement a sitemap to help search engines find important pages, especially for large websites.
2. Clearer Navigation: Simplify the navigation structure for easy search engine crawling. Organize URLs into folders to better organize content.
3. Content Accessibility: Avoid restricting access with search or login forms, allowing search engines to freely access content.
4. Text-Based Content: Focus on using text to convey information rather than relying solely on images or videos, making it easier for search engines to index.
5. Canonical URLs: Use canonical URLs to prevent duplicate content issues and clarify the original page version for search engines.
6. Regular Content Updates: Update content regularly to show website activity and encourage search engines to visit more often.
7. Internal Linking: Use internal links to show the website’s structure to search engines and help users navigate.
8. Limit URL Parameters: Reduce the use of URL parameters to make crawling easier, preferring simple, clean URLs.
9. Header Tags: Use hierarchical header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to organize content and highlight important keywords for search engines.
10. Alt Text: Include descriptive alt text for images to give context to search engines and improve image understanding.
11. Meta Tags: Create informative and keyword-rich meta tags (title, description, keywords) for each page to make content clearer to search engines.
12. JavaScript Usage: Use JavaScript sparingly to improve crawlability and ensure content accessibility without relying on JavaScript.
Understanding Crawl Errors and Solutions
Crawl errors happen when search engines face problems exploring a website, making it hard for content to be indexed and seen. Here are some common crawl errors:
1. DNS Errors: Fix wrong DNS settings to prevent these errors.
2. Server Connection Problems: Solve server setup issues to avoid connection problems.
3. Robots.txt Issues: Correct robots.txt instructions to help search engines crawl freely.
4. URL Errors: Make sure URLs follow proper formats to avoid crawl issues.
5. Mobile-Friendly Concerns: Ensure your site is easy to use on mobile devices to dodge usability problems.
Fixing these common crawl errors ensures search engines can access your content smoothly, boosting your site’s rankings and visibility.
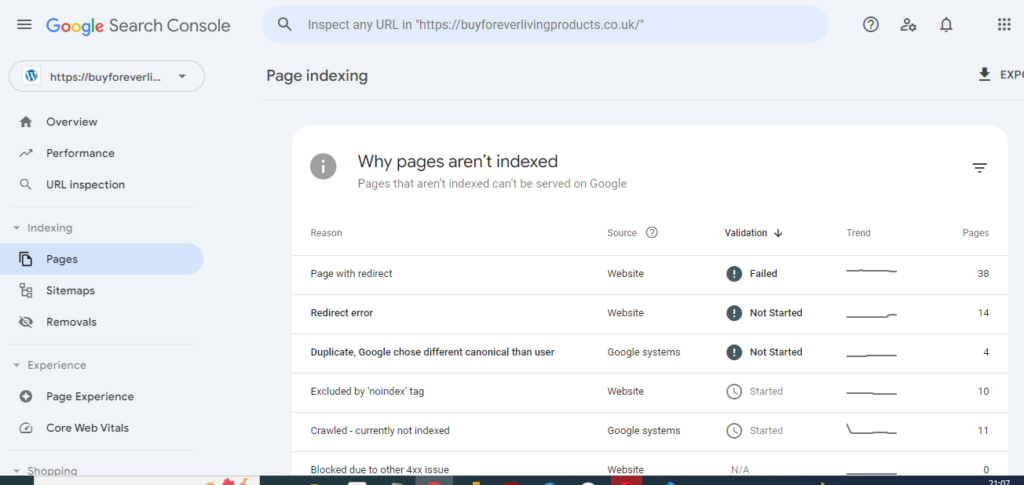
Understanding Indexing Challenges and Remedial Actions Indexing predicaments arise when search engines encounter obstacles while indexing content, limiting its visibility to users. Common indexing quandaries encompass:
1. Duplicate Content: Mitigate indexing dilemmas arising from duplicate content by implementing canonical URLs to designate the primary page rendition.
2. Thin Content: Fortify content substance and value to avert indexing lapses attributable to content insufficiency.
3. Low-Quality Content: Enhance content quality by furnishing comprehensive information, ensuring relevance, and refining meta tag optimization.
4. Canonicalization Issues: Ensure seamless canonicalization execution to obviate indexing ambiguities.
5. Indexing Limits: Streamline content organization and structure to circumvent indexing limits and complexity-related hurdles.
Understanding Indexing Challenges and Remedial Actions in 2024
Indexing predicaments arise when search engines encounter obstacles while indexing content, precluding its visibility to users. Common indexing quandaries encompass:
- Duplicate Content: Mitigate indexing dilemmas arising from duplicate content by implementing canonical URLs to designate the primary page rendition.
- Thin Content: Fortify content substance and value to avert indexing lapses attributable to content insufficiency.
- Low-Quality Content: Enhance content quality by furnishing comprehensive information, ensuring relevance, and refining meta tag optimization.
- Canonicalization Issues: Ensure seamless canonicalization execution to obviate indexing ambiguities.
- Indexing Limits: Streamline content organization and structure to circumvent indexing limits and complexity-related hurdles.
SEO Best Practices for your business in 2024
- Quality Content Creation: Create and share top-notch content that matches what your audience wants.
- Tech Setup for SEO: Make sure your website is fast, works well on mobile, and has a clear map for search engines to find.
- Building Good Links: Get links from reputable sites that relate to your content to boost your website’s credibility and visibility.
- Local Search Optimization: Customize your SEO efforts to attract local customers by using location-specific keywords and being listed in local directories
Dealing with Ranking Challenges and Solutions in 2024
When content doesn’t rank well in search results, it’s often due to:
1. Keyword Issues: Improve rankings by researching and using the right keywords effectively.
2. Backlink Quality: Improve website credibility with good backlinks from relevant sites.
3. Content Quality: Enhance content quality and relevance following best practices.
4. Technical SEO Problems: Fix technical issues like slow site speed or mobile usability.
5. Algorithm Changes: Stay updated on SEO trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
Solution
1. Quality Content Creation: Create and share top-notch content that matches what your audience wants.
2. Tech Setup for SEO: Make sure your website is fast, works well on mobile, and has a clear map for search engines to find.
3. Building Good Links: Get links from reputable sites that relate to your content to boost your website’s credibility and visibility.
4. Local Search Optimization: Customize your SEO efforts to attract local customers by using location-specific keywords and being listed in local directories.
5. Using Website Data: Use tools like Google Analytics to track who visits your site, how they interact with it, and how often they make a purchase, so you can improve your SEO strategy based on real data.
SEO Tools and Resources:
1. Google Search Console: Use Google’s free toolset to monitor and manage website visibility and indexing in Google search results.
2. Google Analytics: Analyze website traffic, behavior patterns, and performance metrics with Google Analytics.
3. Moz: Access Moz’s SEO suite for insights and recommendations to improve website SEO.
4. Ahrefs: Utilize Ahrefs’ SEO toolkit for detailed analysis and insights to enhance search engine visibility.
5. SEMrush: Employ SEMrush’s SEO tools for optimization to improve website search engine performance.
For more in-depth knowledge and practical insights, I encourage you to explore my YouTube channel, where you’ll find video tutorials diving deeper into SEO optimization. These resources provide actionable tips and strategies to propel your SEO efforts to new heights, ultimately driving more traffic and success to your website.
Please contact me if you want to improve your SEO content strategy or need help understanding SEO. I’m an SEO specialist in London who can help you create leads, enhance your online visibility, and reach your digital marketing goals.